How Unlimited Internet Data Has Changed The Face Of Cybercrime?

VoLTE: Voice over LTE is a high-speed wireless communication standard for mobile phones. It has up to three times more voice and data capacity than older 3G UMTS and up to six times more than 2G GSM. With its increased data capacity, users don’t need to use the data very judiciously, and they can keep the internet connection on every time. Due to this, internet-connected devices are always at a higher risk of infection and online fraud. That is the reason users who use VoLTE are the preferred target of threat actors around the world. Jio is one of the mobile operators which uses VoLTE technology.
Quick Heal Security Labs has gone through multiple scams, fake messages, and fake applications that exploit Jio users over the last few years. The below image shows threat actors’ tactics from 2017.
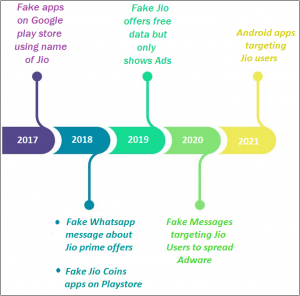
Fig 01.
Let’s take a look in detail.
2017 – FAKE APPS ON GOOGLE PLAY STORE USING THE NAME OF JIO
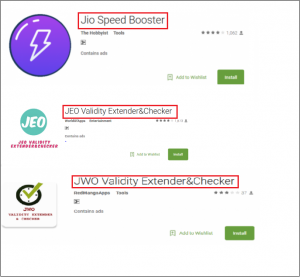
Fig 02.
As shown in Fig. 02, in 2017, Quick Heal Labs spotted few applications on the Google Play store which fake promises like “Speed Boosting” and “Validity Extender and Checker.” These applications trap users into giving their personal information and, in the background, send this information to some third-party websites. Such applications consume a lot of data and show advertisements to the user. Quick Heal was the first to detect such applications with the variants of Android.FakeJeo.
2018 – FAKE WHATSAPP MESSAGES ABOUT JIO PRIME OFFERS
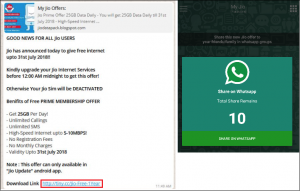
Fig 03.
In 2018, the fake message about Jio prime offers was seen. The message shown in Fig 03 seems legitimate, but it’s a fake message. When a user clicks on the mentioned link, it downloads a fake “Jio Prime app.” When the user opens the application, it takes a random mobile number as input. And, the application pretending that it is connected to a server even mobile data and WIFI connectivity is off.
It asks the user to send this application to 10 WhatsApp groups to earn 50 points. And 100 points were required to activate the offer. After, doing everything the user gets nothing as promised in the message. Malware authors use this tactic to reach out to multiple devices in a short period.
FAKE JIOCOIN APPS ON GOOGLE PLAYSTORE
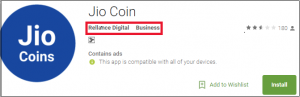
Fig 04.
Quick Heal Security Labs found fake Jio Coin applications from the Google Play Store in the same year, as shown in Fig 04. These apps ask for personal information such as username, mobile number, and email address and show that the user is in a queue for JioCoin. But nothing happens.
2019 – FAKE JIO APPS OFFERS FREE DATA BUT ONLY SHOWS ADVERTISEMENTS

Fig 05.
Again in 2019, Quick Heal Labs found malicious applications that use the legitimate My JIO app icon. Cybercriminals used a similar icon tactic to trap novice users. These applications had similar activities like above. Users who install such malicious applications will not get the offers or free data they promised. Still, their mobile devices will be used to generate advertising revenue by the malware authors.
Quick Heal detects such applications under variants of Android.Fakeapp and Android.GoodNews
2020 – FAKE MESSAGES TARGETING JIO USERS TO SPREAD ADWARE
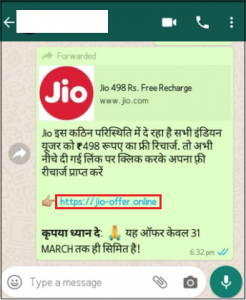
Fig 06.
In 2020, Coronavirus had severely affected people globally. In these pandemic times when the lockdown was imposed, peoples’ dependency on Smart Phones had increased for entertainment and staying connected with the outside world. By taking advantage of this situation, many fake messages were circulated by malware authors to trap unsuspecting users with attractive fake offers like the ones mentioned in Fig 06. The user gets nothing as promised in the message.
2021 – ANDROID APPLICATIONS TARGETING JIO USERS
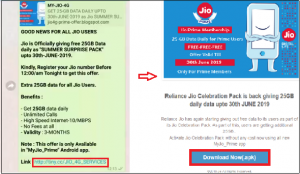
Fig 07. Fake offer messages in 2019.
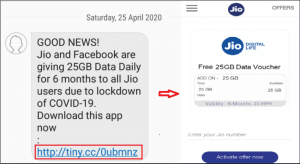
Fig 08. Fake offer messages in 2020.
Similar to previous years, we have seen malicious applications that affected Jio users in 2021 also. We have witnessed malicious applications with similar codes and programs deployed by threat actors on various social media platforms.
In the recent samples, malware authors used new ways and themes for exploitation. This time we have gone through some malicious applications specifically targeting Jio users and spreading fake SMS’s. Let us see how this is done.
When the malicious application is installed in the user’s device, it first performs SIM identification to check the SIM slot used for sending the SMS.
Following operations are performed for identifying SIM cards:
- If Android SDK version >= 22 and READ_PHONE_STATE permission is granted, fetch Sim slot number and Carrier name. Else bring the operator names corresponding to the SIM cards on the current device.
- Checks, if fetched information contains – JIO, AIRTEL, IDEA, VODAFONE, or VI.
- If any of the above strings are present, then check and return the SIM slot number. Else return the value “default”.
Once SIM Identification is made, it identifies the operators of the mobile numbers present in the user’s contact list. As it explicitly targets Jio users. It verifies the contact number in two ways.
As shown in Fig 09, there is a hardcoded list of the first four digits of numbers specific to Jio. All the contacts in the user’s mobile are verified with this list, and contacts are separated, identified as JIO operators in a list.

Fig 09.
The remaining not identified contacts are again checked by sending them to a URL mentioned in Fig 10. Identified contacts of Jio operator again taken in a separate list.
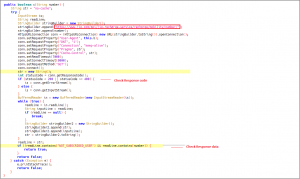
Fig 10.

Fig 11.
The sim slot is identified, and contact numbers of Jio customers are identified from the user’s contact list. The threat actors are now spamming Jio customers by plotting various services and themes to lure them in, as shown in Fig 12.
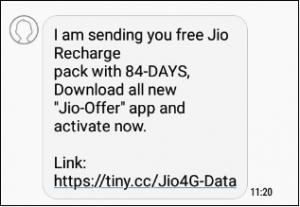
Fig 12.
Quick Heal detects such applications with Android.GoodNews.A
CONCLUSION
- We have seen many unfortunate events in the recent past wherein threat actors from specific countries are actively following trends and social gimmicks of social media platforms to manipulate their victims and gain unauthorized access.
- For example, in the past year, India banned Tik Tok due to security concerns. This was an excellent opportunity for the threat actor to manipulate users actively using Tik Tok with fake messages like “download the new working Tik Tok apk for free” and clickbait them to use the link to deploy their malicious program on the victim’s device.
- And we suggest users not download any applications from third-party sources and never click on any suspicious links even received from their contacts. As seen in this attack, the malicious download links are sent through the user’s existing contact list.
One should have trusted AVs like “Quick Heal Mobile Security for Android” to mitigate such threats and protect you from downloading malicious applications on your mobile device.
TIPS TO STAY SAFE
- Do not click on alien links received through messages or any other social media platforms.
- Download Applications only from trusted sources like Google Play Store.
- Turn off installation from the unknown source option.
- Read the pop-up messages you get from the Android system before Accepting/Allowing any new permissions.
- Malware authors spoof original application’s names, icons, and developer names. So, make sure you are downloading simple applications only.
- For enhanced protection of your phone, always use a good antivirus like Quick Heal Mobile Security for Android.



No Comments, Be The First!