Future Watch II: Rogue SSL certificates on the rise
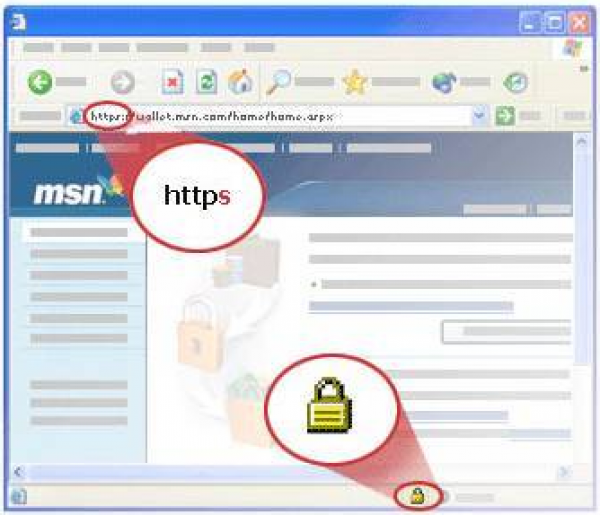
Continuing with our series of predicting potential security threats, this post delves into rogue SSL certificates. This attack vector allows phishers and social engineers to gain complete trust of their victims, the prospects of which are quite frightening. SSL (Secure Socket Layer) certificates are present on pages where a user needs to enter private data, like passwords and credit/debit card details. The best way to identify SSL secured pages is to look for “HTTPS” before the URL on the address bar. Additionally, a padlock symbol in the address bar (or in the lower right corner of the browser) also verifies the same.
The SSL certificate validates a website and lets the user place his trust in any page where he enters his details. While this is useful in order to avoid fake phishing pages, there are several risks that accompany this process, which exploited could create unfavorable scenarios. Let’s take a look at these potential risks:
Victims Trust
Since the victim places his/her trust on the webpage based on several visual signs, rogue certificates tend to offset the trust factor. Once the trust is established, the victim feels comfortable giving out any information that is asked of him and does not heed several warning signs. This allows the attacker to gather data within a matter of seconds. It also gives him the option to stay undetected for as long as he possesses the ‘key’.
Identity Theft
An unsuspecting user, who enters his details on a page with a rogue SSL certificate, is susceptible to the risk of identity theft. Once a phisher gains the identity of a victim, he can do as he pleases with this identity. The data thus gathered could be sold to other malicious parties or be put to ill-use by the attacker. The victim feels that he is carrying out a transaction with a secured party, but in reality, the attacker is controlling the entire scenario.
Spoof Websites
Some attackers reroute victims to spoof websites with the help of rogue ISPs. This is a highly precarious situation as it provides the attacker with tons of information that a victim willingly parts with. For instance, a fake Gmail login page or a fake banking transaction page will successfully convince many people to enter their password and card details respectively. This will open up massive attack vectors. This form of an attack is also known as a MITM (man in the middle) attack.
It is not just individual users who are susceptible to rogue certificates. Other parties like public-key infrastructure, e-commerce websites, host-based technologies like whitelisting (or application control) and secure web browsers are also at risk. Rogue state agencies can also use this technique to monitor their citizens and gather large databases of information about their activities and other details.
We advise Quick Heal users to be more vigilant while browsing the web and especially while entering their details. Social engineering techniques are highly effective and innovative today. So the only way to not fall prey to them is to be alert and maintain an updated version of the best virus protection software.
2 Comments
how ican identify Rogue SSL certificates ?
Hi,
The steps mentioned in the post above will be sufficient to spot rogue SSL certificates. Additionally, you can also refer to this blog post – https://blogs.quickheal.com/faqs-on-ssl-certificates-and-their-importance/.
Regards.