Hackers Launching Multiple Attacks using One Email

What makes cybercriminals more notorious is that they do not stay idle. They keep themselves busy in improving their game and formulating newer methods to trap their preys. A case in point is a recent observation made by Quick Heal Labs where attackers are using a new open source exploit called ‘CVE-2016-0189’ for Internet Explorer. In this malicious campaign, attackers are using exploits of Microsoft Office and Internet Explorer in a single email instead of multiple ones. This campaign was active in August 2016 and was found to be targeting some private organizations in India.
What is the reason behind using multiple exploits in one email?
To increase the success rate of exploitation and execution of the delivered malware on the victim’s machine against security vulnerabilities present in Internet Explorer and Microsoft Office.
A mashup of different exploits to cause double damage
In this campaign, attackers combined an Internet Explorer exploit called ‘CVE-2016-0189’ with old Microsoft Office exploits called ‘CVE-2012-0158’ and ‘CVE-2015-2545’. This was done for to increase the chances of a reliable execution of the malware.
How does this attack begin?
The victim receives an email containing HTML and RTF files as attachments (fig 1).
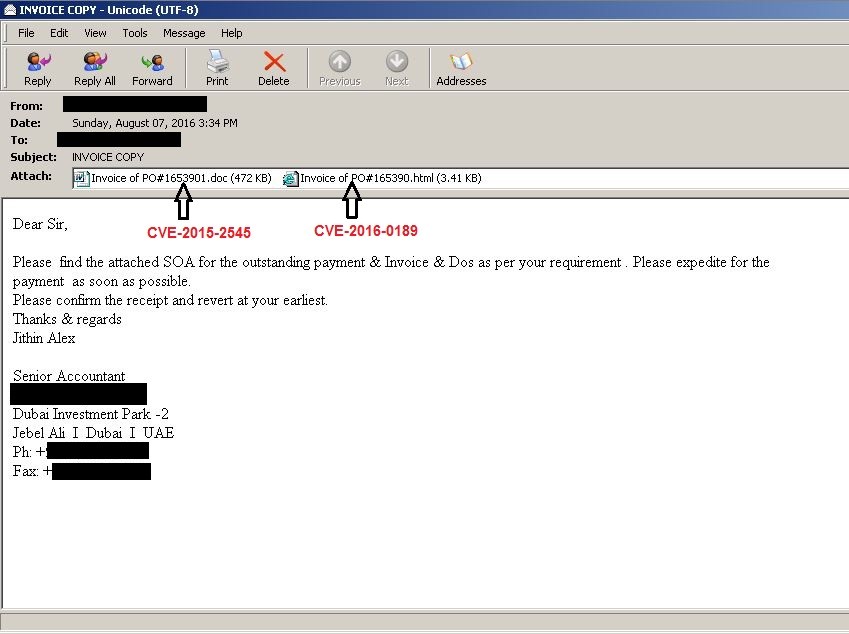
Fig 1
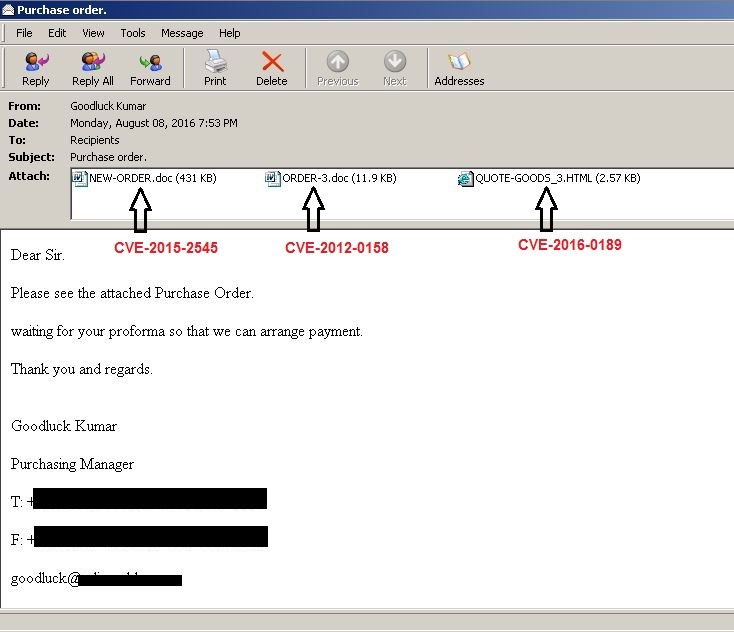
Fig 2
If the receiver’s computer has an unpatched (outdated) version of Microsoft Office or Internet Explorer, then opening the attached files exploit the vulnerabilities in these applications, downloading and executing the malware on the victim’s machine.
Both the RTF and HTML exploit download the malware payload from the same URL path.
Some of the URLs used for downloading the malware are as follows:
- hxxp://www.pgathailand.com/overnight[.]exe
- hxxp://maxcoffe.co/famozsymboss[.]exe
- hxxp://ksmovement.pl/ComCom[.]exe
Quick Heal detects the downloaded malware as “TrojanPWS.ZBot” and “Trojan.Dynamer”. These are designed to steal sensitive information stored on the infected machine and they can also download and install other malware components.
Download the PDF file below for the technical analysis of this campaign
How to stay safe against such attacks
- Apply all recommended security updates for your computer’s Operating System and all other programs such as Adobe, Java, Internet Browsers, etc.
- Do not click on links or download attachments that arrive in emails from unwanted or unexpected sources.
- Even if such emails seem to be from a known source, it is better to call up the sender and verify them first.
- Install an antivirus software that gives has multilayered protection. It must have Email Security that can block fake, infected or phishing emails. And it should also have a strong Web Protection feature that can automatically block access to websites that could be infected with malware.
1 Comment
Thanks