Top Cyber-security trends affecting Windows users during 2019

The year 2019 saw several new and recurring incidences of cyber-attacks, giving enterprises sleepless nights and the general public a run for security cover. However, there were a few trending malware that kept creating havoc and continued to keep the security experts on toes!
Here’s a quick insight on few such trending cyber-attacks on Windows operating system in 2019:
1. STOP Ransomware Assaulting Systems with Cracks!
With 180+ extensions in the wild, STOP (.djvu) can be considered as the most widespread & trending Ransomware of year 2019. The infection vector for this ransomware is particularly cracked software downloaded from internet. In cases of cracked software, user tends to ignore the antivirus detection and executes it by taking risk, which is the main reason behind its success.
According to observations by Quick Heal Security Labs, cracked files or activators for different software like Tally, Minecraft, Nero 7, Autocad, Adobe Photoshop, Internet Download Manager, Cyberlink Media Suite, Microsoft Office, VMware Workstation, DreamWeaver, Corel Draw Graphic Suite, Quick Heal Total Security, Ant Download Manager, IBEESOFT Data Recovery, Any Video Converter Ultimate were seen spreading this ransomware.
With the continuous introduction of newer extensions, STOP author keeps on adding different software cracks to their infection list. For every new extension, their online CnC servers stay active for a certain period only. After that, it switches to another extension. The usual ransom amount is $980 for which they offer concession of 50% if paid within 48 hours of encryption.
To stay protected we advise our users:
- Do not use or download cracked software.
- Do not install software from untrusted sources.
- Always keep your Anti-virus definitions up-to-date.
- Do not allow suspicious or malicious applications to run.
- Backup your data.
2. Emotet: Continues aggressive spreading over the globe
Emotet is now a familiar name in cyber security world. It is the most severe threat since last couple of years. After a prolonged break in mid-2019, a new variant of Emotet was observed by Quick Heal Security Labs with a new wrapper blending and some complex obfuscation techniques.
An interesting thing noticed was the change in its communication pattern i.e. previously it was sending all data in cookie header of GET requests, while now it was found sending all data as part of POST requests. This again goes on to emphasize that the choice of advanced layer of protection is critical over conventional signature-based approach, to stop such complex malware campaigns.
Emotet is continuing its faith on malspams for propagation. Interestingly, it uses geographically targeted emails according to local-language lures and brands. Also, it chooses current events for crafting of spams like at the end of 2019, Halloween themed spamming emails were observed.
Few security measures to follow:
- Don’t open any link in the mail body sent by an unknown source.
- Don’t download attachments received by any untrusted source.
- Always turn on email protection of your antivirus software.
- Don’t enable ‘macros’ or ‘editing mode’ upon execution of the document.
3. Use of MySQL for attacks on enterprises
Database servers like MySQL, MongoDB, MSSQL, are used for storing precious business data. But unfortunately, not everyone is conscious about the security of this stored business data. In fact, approximately 90% of these applications have credentials like root:root, scott:tiger. In some cases, we observed people even don’t use credential for database server’s root account.
MySQL has been a regular target for malicious users or hackers wanting to exploit and steal data. This type of exploits can be serious; it can include putting malicious software on your web server and using the website to host malware. MySQL server runs as a service, so it runs with system privilege. If attacker enters the network using MySQL, it executes with system privileges, so it can access everything on infected host without any vulnerability. Now once attacker gets access to MySQL database, it can manipulate your data, delete it or steal it.
Attackers can play with the database like they can drop existing table and create new table for malicious purpose or use MySQL as an entry into Linux or Windows system and then drop a backdoor. Any application executed by mysqld.exe will run with system privileges and can be used to launch file-less malware attacks. Till now, we have seen these MySQL attacks being used for dropping ransomware and Virus infector which ultimately drops another backdoor with IoT capabilities.
4. Living-Off-the-Land tactics used by Attackers
In the recent years, there has been an increase in use of Living-off-the-Land (LoLBins) tactics. Attackers are actively using windows native/system tools to carry out their attacks. Using LoLBins, attackers can easily bypass traditional security solutions, bypass application whitelisting, execute files-less attacks and download another payload. Below are widely used LoLBins attacks observed by Quick Heal Security Lab:
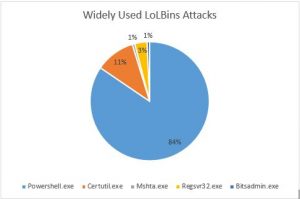
- Powershell.exe – PowerShell is a command-line interface utility which can be used by an attacker to perform several actions such as code execution, discovery of network, information, etc.
- Certutil.exe – Certutil is a command-line utility in windows that is used to obtain certificate information and configure Certificate Services. Actors used this tool to download encoded payload.
- Mshta.exe – Mshta.exe is a utility responsible for executing .HTA (Microsoft HTML Application) files. Attackers execute malicious HTA files like JavaScript or VBScipt files through legitimate applications.
- Regsvr32.exe – Regsvr32.exe is a Windows command-line utility used to register and unregister object linking and embedding of controls including dynamic link libraries (DLLs). Attackers use this utility to bypass process whitelisting functionality to load COM scriptlets for executing malicious DLLs.
- Bitsadmin.exe – Bitsadmin.exe is component for Windows Background Intelligent Transfer Service. Attackers use this tool to download, upload and execute payload.
Note: For a more detailed report on the trending cyber-attacks of 2019, look out for our annual threat report to be out soon…
No Comments, Be The First!